# 第3章 资源输入输出
# 资源处理流程
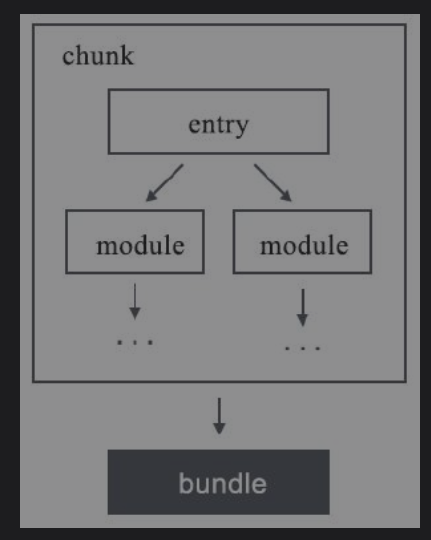
- 需要有一个或多个入口(enrty)。
- 存在依赖关系的模块会在打包时被封装为一个chunk(代码块),里面有各个模块。
- 由chunk得到的打包产物称为bundle。
# 配置资源入口
# context
context是资源入口的路径前缀,必须使用绝对路径。可以省略,默认是当前工程的根目录。主要目的是让entry更加简洁。
module.exports = {
context: path.join(__dirname, './src'),
entry: './index.js'
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# entry
# 字符串类型入口
entry: './src/index.js';
1
# 数组类型入口
数组的作用是将多个资源预先合并,数组最后的元素会作为实际的入口路径
entry: ['babel-polyfill', './src/index.js']
1
相当于:
entry: './src/index.js'
// index.js
import 'babel-polyfill';
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# 对象类型入口
定义多入口必须使用对象形式。
entry: {
index: './src/index.js',
lib: './src/lib.js'
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
对象的属性值也能为字符串或数组。
# 函数类型入口
entry: () => './src/index.js';
entry: () => ({
index: [],
lib: '',
})
entry: () => new Promise(() => {})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 实例
webpack默认配置中, 当一个bundle大于250kb时会认为体积过大,打包时会发生警告。
# 提取vendor
一个js文件体积过大,一旦产生代码更新,用户都要重新下载整个资源文件,影响页面性能。
vendor一般是指工程所使用的库、框架等第三方模块集中打包产生的bundle。
entry: {
app: './src/app.js',
vendor: ['react', 'reacnt-dom']
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
打包时可以通过optimization.splitChunks将app和vendor两个chunk中的公共模块提取出来。
由于vendor仅包含第三方模块,不会经常变动,可以有效利用客户端缓存,提高页面渲染速度。
# 多页应用
减小资源的体积,每个页面都加载各自必要的逻辑。
entry: {
pageA: './pageA.js',
pageB: './pageB.js',
pageC: './pageC.js',
vendor: ['react', 'react-dom']
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
# 配置资源出口
# filename
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js'
//filename: './js/bundle.js'
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
filename可以是bundle的名字,也可以是一个相对路径,路径中如果不存在会创建该目录。
// 多入口
{
entry: {
app: './src/app.js',
vendor: './src/vendor.js'
}
output: {
filename: '[name]-[chunkhash].js'
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# path
path资源输出位置,要求值必须为绝对路径。
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist');
}
1
2
3
2
3
# publicPath
public用来指定资源的请求位置。
// 假设当前HTML地址为 https://example.com/app/index.html
// 异步加载的资源名为 0.chunk.js
// HTML相关
publicPath: '' // 实际路径https://example.com/app/0.chunk.js
publicPah: './js' // 实际路径https://example.com/app/js/0.chunk.js
publicPah: '../assets/' // 实际路径https://example.com/aseets/0.chunk.js
// Host相关
publicPath: '' // 实际路径https://example.com/app/0.chunk.js
publicPah: './js' // 实际路径https://example.com/app/js/0.chunk.js
publicPah: '../assets/' // 实际路径https://example.com/aseets/0.chunk.js
// HTML相关
publicPath: '/' // 实际路径https://example.com/0.chunk.js
publicPah: '/js/' // 实际路径https://example.com/js/0.chunk.js
// CDN相关
publicPath: 'https://cdn.com/' // 实际路径https://cdn.com/0.chunk.js
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
webpack-dev-serve配置中也有一个publicPath,它的作用是指定静态资源路径:
devServer: {
publicPath: '/assets/'
}
1
2
3
2
3