# 第4章 函数
- 一般来说,编程就是将一组需求分解成一组函数与数据结构的技能。
- 由互相关联的原型组成的结构就是原型链。
- 一个函数总会返回一个值。如果没有指定返回值,就会返回undefined。
- 内部函数或对象在函数外被调用执行时,可以访问所在的词法作用域,这种状态是闭包。
- es6已经支持尾调用优化了,尾递归介绍 (opens new window)
- 原型链图
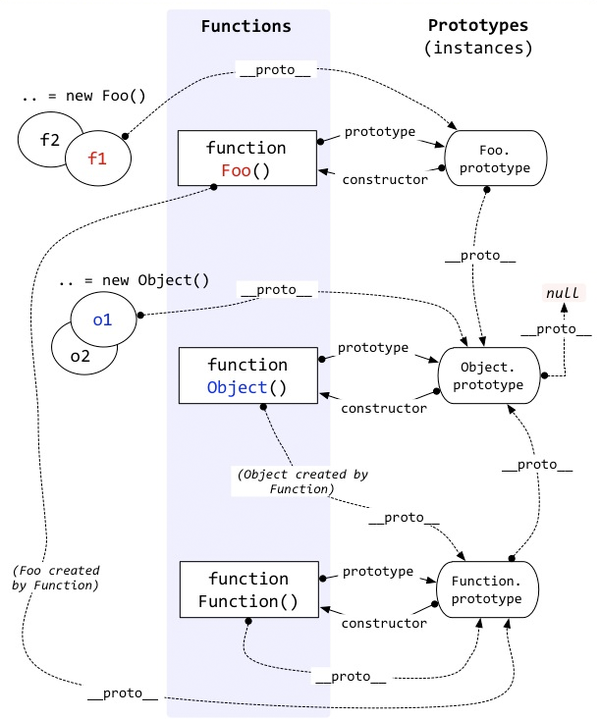
# constructor
function name(params) {
}
console.log(name.prototype.constructor===name);//true
console.log((new name).__proto__.constructor===name);//true
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# js中有4种调用模式
方法调用模式,函数调用模式,构造器调用模式,apply调用模式
# 1. 方法调用模式
当一个函数被保存为对象的一个属性时,称它为一个方法
var obj={
a:'a',
methed:function(){
console.log(this.a)//a
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
2
3
4
5
6
方法可以使用this访问自己所属的对象。this到对象的绑定发生在调用的时候。
# 2. 函数调用模式
这种模式调用时,this绑定到全局对象,所以会导致下面问题
var a='b';
obj.double=function(){
var that=this;
var help=function(){
console.log(this.a);//b
console.log(that.a);//a
}
help();//这里调用时函数调用模式,this指向全局
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 3. 构造器模式
如果一个函数前加上new来调用,那么this会绑定到那个新对象上。
function x(){this.c='a';this.b=this.val;};
x.prototype.val='val';
var y=new x();
console.log(y);//{c: "a", b: "val",__proto__.val:'val'};
y.__proto__.val='y';
var z=new x();
console.log(z)//{c: "a", b: "y",__proto__.val:'y'};
console.log(z.__proto__.val)//y
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 4. apply调用模式
var objx={
a:'aaa'
}
obj.methed.apply(objx);//aaa
1
2
3
4
2
3
4
# arguments
arguments是具有迭代器的类数组对象
function yyy(a,b,c){
//arguments是具有迭代器的类数组对象
console.log(arguments)//Arguments(5){0:1,1:2,2:3,3:4,length:4,Symbol(Symbol.iterator): ƒ values()}
}
yyy(1,2,3,4);
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
# Number和Function关系
Function.prototype.d='d';
Function.prototype.m=function(c){console.log(c,111);}
console.log((new yyy()).d);//undefined 实例上取不到Funtion原型上的值。yyy原型上的Function的原型上d值为d
console.log(yyy.d);//d
console.log(Number.d)//d Number原型上的Function的原型上的d值为d
console.log(Number.m('c'))//c,111
console.log(Object.d)//d
// 内建对象原型关系:
// Object->Function->Object
// Number->Function->Object
// String->Function->Object
// Boolean->Function->Object
// Array->Function->Object
// RegExp->Function->Object
// Date->Function->Object
// Math->Object
Date.prototype===new Date().__proto__//true
// {constructor: ƒ, toString: ƒ, toDateString: ƒ, toTimeString: ƒ, toISOString: ƒ, …}
new Date().__proto__.toString===Date.prototype.toString//true
// ƒ toString() { [native code] }
function xxx(params) {
}
xxx.prototype.ooo='0';
console.log(new xxx().__proto__.ooo===xxx.prototype.ooo);//true
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
# 模块
//产生了一个闭包
function module(){
var mo='mo'
return {
x:1,
y:mo,//'mo'
that:function (params) {
console.log(this)
},
_this:this//Window
}
// return function(){
// console.log(this)//Window
// }
}
var mo=module();
// mo()//Window
mo.that()//{x:1,y:'mo',that:function(params){}}
console.log(mo)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# A.prototype=new B();
function zzz(){
this.name='a'
}
zzz.prototype.getname=function(){
return this.name;
}
function ttt(){
this.name='ttt'
}
ttt.prototype.getnamex=function(){
return this.name;
}
zzz.prototype=new ttt();
console.log(zzz);
// ttt {name: "ttt"}
// name: "ttt"
// __proto__:
// getnamex: ƒ ()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18